Unlock the Potential of Tiny AI Agents
In today’s digital landscape, there’s an incredible opportunity to create and profit from small, specialized AI agents. These “Tiny AI Agents” deliver immense value without the complexity or scale of full-blown autonomous AI systems.
In this guide, I’ll show you step-by-step how to build these AI agents and transform them into thriving online digital products. The best part? Each individual AI agent can generate three distinct income streams for you!
Here’s a more streamlined rewrite of your post:
What Are Tiny AI Agents?
Before diving into the technical aspects, let’s clarify what a “tiny AI agent” is.
A tiny AI agent is a specialized, pre-built system designed to perform specific tasks based on defined parameters and inputs. Unlike comprehensive AI systems, these agents are:
- Task-oriented: They excel at a single task.
- Quick to build: Development can take just a few hours.
- High-value: They effectively solve real-world problems.
- Easy to monetize: They can be packaged as diverse digital products.
While some may argue these are more “AI workflows” than true agents (since they lack full autonomous reasoning), their real significance lies in their ability to deliver quick and impactful results.
For those interested in creating fully autonomous agents with reasoning capabilities, check out my detailed guide.
The Core Engine: LLM Router
The secret sauce behind these tiny agents is the LLM Router—a decision-making module that selects the best course of action based on user inputs.
This functionality, now available in my open-source Python package SimplerLLM, enables even non-experts to build these agents with ease. Here’s how it works:

- Takes user input
- Analyzes input against predefined templates
- Chooses the optimal path for processing
- Directs the workflow accordingly
This method allows tiny agents to make intelligent decisions without requiring complex autonomous systems.
A Practical Example: Tweet Generator
Let’s put theory into action with a simple example—a tweet generator. This tiny AI agent pulls content from sources like YouTube videos, blog posts, or raw text and transforms it into engaging tweets tailored to your personal style.
This agent has three core components:
- Content Input — What the tweets will be about
- Templates — Tweet structures proven to perform well
- Profile — Your personal style, background, and voice
Step 1: Set Up The Core Components
First, let’s import the necessary libraries and set up our environment:
[collapsible_blur points=”10″]
# Import necessary libraries
import re
import requests
from typing import List
from enum import Enum
from pydantic import BaseModel
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Import SimplerLLM libraries
from SimplerLLM.language.llm_addons import generate_pydantic_json_model_async
from SimplerLLM.language.llm_router import LLMRouter
from templates import get_template_choices
[/collapsible_blur]
Step 2: Define Our Models
Next, we’ll define the structure for our input sources and output:
[collapsible_blur points=”10″]
# Define source types
class SourceType(str, Enum):
"""
Enum for different types of content sources.
- YOUTUBE: Content from a YouTube video (will extract transcript)
- BLOG: Content from a blog post (will scrape paragraphs)
- TEXT: Direct text input
"""
YOUTUBE = "youtube"
BLOG = "blog"
TEXT = "text"
# Define the tweet output model using Pydantic
class TweetOutput(BaseModel):
"""
Pydantic model for generated tweets output.
- tweets: List of generated tweets
"""
tweets: List[str]
[/collapsible_blur]
Step 3: Extract Content From Different Sources
Our agent needs to be flexible in accepting content from various sources:
[collapsible_blur points=”10″]
async def extract_content(source_type: SourceType, content: str) -> str:
"""
Extract content from different sources.
Parameters:
- source_type: Type of content source (YouTube, blog, or text)
- content: The content identifier (URL or text)
Returns:
- Extracted content as a string
"""
# Case 1: If source is YouTube, extract the transcript
if source_type == SourceType.YOUTUBE:
# Extract the video ID from the YouTube URL
match = re.search(r"(?:youtube\.com/watch\?v=|youtu\.be/|youtube\.com/shorts/)([\w-]+)", content)
if not match:
raise ValueError("Invalid YouTube URL format")
video_id = match.group(1)
# Get the transcript using the video ID
transcript = await get_youtube_transcript(video_id)
return transcript
# Case 2: If source is a blog, scrape the paragraphs
elif source_type == SourceType.BLOG:
# Make a request to the blog URL
response = requests.get(content)
# Parse the HTML content
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
# Extract all paragraphs and join them
return " ".join([p.text for p in soup.find_all('p')])
# Case 3: If source is direct text, return it as is
elif source_type == SourceType.TEXT:
return content
# Default case: If source type is not recognized, return the content as is
return content
[/collapsible_blur]
Step 4: Implement The LLM Router For Template Selection
This is where the magic happens – the router analyzes the content and selects the most appropriate tweet templates:
[collapsible_blur points=”10″]
def select_best_templates(content: str, llm_instance) -> List[dict]:
"""
Select the best templates for the given content using LLMRouter.
Parameters:
- content: The content to generate tweets from
- llm_instance: The language model instance
Returns:
- List of selected templates with their metadata
"""
# Create a new LLMRouter instance
router = LLMRouter(llm_instance=llm_instance)
# Add template choices to the router
router.add_choices(get_template_choices())
# Create a prompt that instructs the LLM to select appropriate templates
selection_prompt = f"""
Please analyze the following content and select the most appropriate tweet templates that would work well for creating engaging tweets about this topic:
CONTENT:
{content}
Select templates that:
1. Match the tone and subject matter of the content
2. Would help highlight the key points effectively
3. Would resonate with the target audience for this topic
"""
# Get the best 3 templates using the router
top_templates = router.route_top_k_with_metadata(
selection_prompt, # Using the instructional prompt
k=3, # Select top 3 templates
metadata_filter={} # No filtering
)
# Extract the selected templates with their metadata
selected_templates = []
for result in top_templates:
template_index = result.selected_index
template_content, template_metadata = router.get_choice(template_index)
selected_templates.append({
"template": template_content,
"metadata": template_metadata
})
return selected_templates
[/collapsible_blur]
Step 5: Generate Tweets Based On Content, Templates, And Profile
Finally, we use the selected templates and profile to generate personalized tweets:
[collapsible_blur points=”10″]
async def generate_tweets(content: str, templates: List[dict], llm_profile: str, llm_instance) -> TweetOutput:
"""
Generate tweets based on content, templates, and LLM profile using SimplerLLM.
Parameters:
- content: The content to generate tweets from
- templates: List of selected templates with their metadata
- llm_profile: The LLM profile text
- llm_instance: The language model instance
Returns:
- TweetOutput object with generated tweets
"""
# Create a prompt for the LLM
prompt = f"""
# TASK: Generate 3 Viral X Tweets
You are a social media expert specializing in creating high-engagement Twitter content.
## CONTENT TO Create Tweets based on:
```
{content}
```
## TEMPLATES TO FOLLOW
Use these templates as structural guides for your Tweets. Each Tweet should follow one of these templates:
```
{templates[0]['metadata']['format']}
{templates[1]['metadata']['format']}
{templates[2]['metadata']['format']}
```
## LLM PROFILE (Your background and style)
```
{llm_profile}
```
## REQUIREMENTS
- Create exactly 3 Tweets, each following one of the provided templates
- Each Tweet must be around 8-10 tweets under 280 characters each
- Include relevant hashtags where appropriate (max 2-3)
- Focus on providing value or insights that would make users want to share
- Adapt the style to match the LLM profile
## OUTPUT FORMAT
Provide 3 ready-to-post Tweets that follow the templates and capture the essence of the content.
"""
# Generate tweets using SimplerLLM's pydantic model generation
response = await generate_pydantic_json_model_async(
model_class=TweetOutput,
prompt=prompt,
llm_instance=llm_instance
)
return response
[/collapsible_blur]
Step 6: Putting It All Together
Our main function orchestrates the entire workflow:
[collapsible_blur points=”10″]
async def main(source_type: SourceType, content: str, llm_profile_path: str, llm_instance):
"""
Main function to demonstrate the tweet generation flow.
Parameters:
- source_type: Type of content source (YouTube, blog, or text)
- content: The content identifier (URL or text)
- llm_profile_path: Path to the LLM profile text file
- llm_instance: The language model instance
"""
# 1. Extract content from the source
print(f"Step 1: Extracting content from {source_type.value} source...")
extracted_content = await extract_content(source_type, content)
# 2. Select the best templates using LLMRouter
print("\nStep 2: Selecting best templates with LLMRouter...")
templates = select_best_templates(extracted_content, llm_instance)
# 3. Read the LLM profile
print("\nStep 3: Reading LLM profile...")
llm_profile = read_llm_profile(llm_profile_path)
# 4. Generate tweets using SimplerLLM
print("\nStep 4: Generating tweets with SimplerLLM...")
tweet_output = await generate_tweets(extracted_content, templates, llm_profile, llm_instance)
# 5. Display the results
print("\nGenerated Tweets:")
for i, tweet in enumerate(tweet_output.tweets, 1):
print(f"\nTweet {i}:")
print(tweet)
[/collapsible_blur]
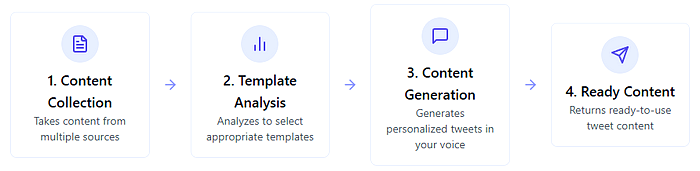
With just these few components, we’ve built a functional AI agent that:
- Takes content from multiple sources
- Analyze it to select appropriate templates
- Generates personalized tweets in your voice
- Returns ready-to-use content
Expanding the API Monetization Approach
✅ Self-Hosting vs. API Marketplaces – While RapidAPI is a great option, consider hosting your API on your own platform (e.g., using Stripe for payments). This avoids marketplace fees and gives you full control.
✅ Subscription Models – Instead of just usage-based pricing, offer monthly or yearly plans with added benefits (e.g., priority access, advanced features).
✅ Freemium Upsell Strategy – Let users test your API for free with limits, then guide them toward premium plans.
✅ Affiliate Partnerships – Partner with other developers or platforms and offer commission-based referrals for API subscriptions.
Are you currently listing APIs on RapidAPI, or are you looking to set up your own monetization system? 🚀
2. Building a SaaS with WordPress
Another effective way to monetize your AI agent is by turning it into a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) using WordPress. This approach allows you to create a user-friendly platform without heavy coding.
How to Set It Up:
- Set up a WordPress site with a membership or subscription plugin.
- Build an interface where users can interact with your AI agent.
- Implement a token/credit system to manage usage limits.
- Market your SaaS to attract paying users.
Why the SaaS Model Works:
✔️ Recurring Revenue – Earn consistent income through subscriptions.
✔️ Customer Ownership – Build direct relationships with users.
✔️ Scalability – Add more AI tools over time to increase value.
By combining WordPress with the right plugins (like myCred for credits or MemberPress for subscriptions), you can turn any AI agent into a profitable SaaS business.